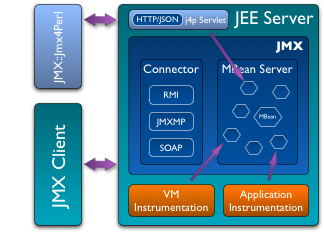
Jmx4Perl provides an alternative way of accessing Java JEE Server management interfaces that are based on JMX (Java Management Extensions). It is an agent-based approach where a small Java Web application (approx. 150k) deployed on the application server provides HTTP/JSON-based access to JMX MBeans registered within the application server. It is set up from a handful of Perl modules, which can be integrated seamlessly in your own Perl programs. It includes a sample Nagios check command utilizing JMX::Jmx4Perl as well as the jmx4perl tool, which allows for access to JMX information via the command line. j4psh is a readline based JMX shell with context sensitive command completion and syntax highlighting.
Benefits of this approach compared to the traditional way of accessing JMX remotely via JSR 160 connectors are:
Jmx4perl can be operated in a proxy mode where a dedicated proxy server accesses the target platform via JSR-160 JMX remoting. This allows for an agentless operation without the need of installing any extra software on the target server.
Beside these technical advantages, the JMX Nagios Plugin check_jmx4perl provides also a rich feature set:
This plugin has been tested on JBoss 4.2.3 GA & 5.1.0 GA, Oracle Weblogic 9.2 MP3 & 10.0.2.0, IBM Websphere 6.1 & 7.0, Jonas 4.10.3 (with Jetty 5.1.10 and Tomcat 5.5.26), Apache Geronimo 2.1.4 (Jetty 6 and Tomcat 6), Glassfish 2.1 & v3, Apache Tomcat 4.1.39, 5.5.27 & 6.0.18 and Jetty 5.1.15 & 6.1.18 (with JMX enabled). Beside these, it should work on any Servlet Container running on at least Java 1.5.
check_jmx4perl is part of a larger distribution, jmx4perl. In addition to this Nagios plugin, jmx4perl contains tools for exploring and examing the available JMX MBeans on the JEE-Server so that it is easy to discover the MBeans and attributes worth monitoring.
A Mule agent for deploying on the Mule ESB Server is available, too.
You can find Jmx4Perl at CPAN.